 题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
December 12th, 2015的中文是()
A.2015年12月12日
B.12月12日2015年
C.2015年12日12月
D.12日12月2015年
 答案
答案
A、2015年12月12日
 如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
 题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
A.2015年12月12日
B.12月12日2015年
C.2015年12日12月
D.12日12月2015年
 答案
答案
A、2015年12月12日
 如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
 更多“December 12th, 2015的中文是()”相关的问题
更多“December 12th, 2015的中文是()”相关的问题

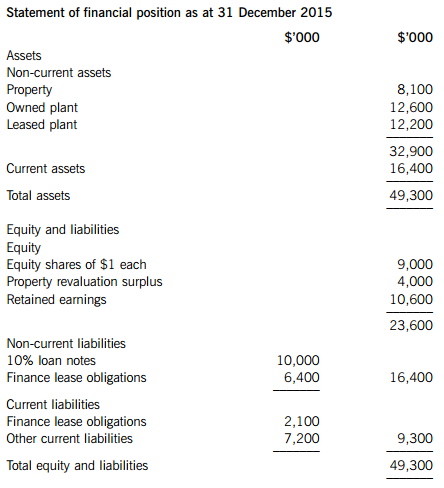
Required:
(a) Prepare for Nonat Co the equivalent ratios to those of its sector.
Note: The finance lease obligations should be treated as debt in the ROCE and gearing calculations. (6 marks)
(b) Analyse the financial performance and position of Nonat Co for the year to 31 December 2015 in comparison to the sector averages. (9 marks)
Triangle Ltd is registered for value added tax (VAT) and uses the annual accounting scheme.
For the year ended 31 December 2015, the net VAT payable by Triangle Ltd was £73,500.
For the year ended 31 December 2014, the net VAT payable by Triangle Ltd was £47,700.
What monthly payments on account of VAT must Triangle Ltd make in respect of the year ended 31 December 2015 prior to submitting its VAT return for that year?
A.Nine monthly payments of £7,350
B.Nine monthly payments of £4,770
C.Ten monthly payments of £4,770
D.Ten monthly payments of £7,350
Which would be treated as a NON-adjusting event under IAS 10 Events After the Reporting Period?
A.A public announcement in April 2015 of a formal plan to discontinue an operation which had been approved by the board in February 2015
B.The settlement of an insurance claim for a loss sustained in December 2014
C.Evidence that $20,000 of goods which were listed as part of the inventory in the statement of financial position as at 31 March 2015 had been stolen
D.A sale of goods in April 2015 which had been held in inventory at 31 March 2015. The sale was made at a price below its carrying amount at 31 March 2015
During the year, the directors reviewed the useful lives and depreciation rates of all classes of plant and machinery. This resulted in an overall increase in the asset lives and a reduction in the depreciation charge for the year.
Inventory is held in five warehouses and on 28 and 29 December a full inventory count will be held with adjustments for movements to the year end. This is due to a lack of available staff on 31 December. In October, there was a fire in one of the warehouses; inventory of $0·9 million was damaged and this has been written down to its scrap value of $0·2 million. An insurance claim has been submitted for the difference of $0·7 million. Venus is still waiting to hear from the insurance company with regards to this claim, but has included the insurance proceeds within the statement of profit or loss and the statement of financial position.
The finance director has informed the audit manager that the October and November bank reconciliations each contained unreconciled differences; however, he considers the overall differences involved to be immaterial.
A directors’ bonus scheme was introduced during the year which is based on achieving a target profit before tax. In order to finalise the bonus figures, the finance director of Venus would like the audit to commence earlier so that the final results are available earlier this year.
Required:
Describe FIVE audit risks, and explain the auditor’s response to each risk, in planning the audit of Venus Magnets Co.
Required:
(a) (i) Discuss the criteria which must be met for a contract with a customer to fall within the scope of IFRS 15. (5 marks)
(ii) Discuss the four remaining steps which lead to revenue recognition after a contract has been identified as falling within the scope of IFRS 15. (8 marks)
(b) (i) Tang enters into a contract with a customer to sell an existing printing machine such that control of the printing machine vests with the customer in two years’ time. The contract has two payment options. The customer can pay $240,000 when the contract is signed or $300,000 in two years’ time when the customer gains control of the printing machine. The interest rate implicit in the contract is 11·8% in order to adjust for the risk involved in the delay in payment. However, Tang’s incremental borrowing rate is 5%. The customer paid $240,000 on 1 December 2014 when the contract was signed. (4 marks)
(ii) Tang enters into a contract on 1 December 2014 to construct a printing machine on a customer’s premises for a promised consideration of $1,500,000 with a bonus of $100,000 if the machine is completed within 24 months. At the inception of the contract, Tang correctly accounts for the promised bundle of goods and services as a single performance obligation in accordance with IFRS 15. At the inception of the contract, Tang expects the costs to be $800,000 and concludes that it is highly probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognised will occur. Completion of the printing machine is highly susceptible to factors outside of Tang’s influence, mainly issues with the supply of components.
At 30 November 2015, Tang has satisfied 65% of its performance obligation on the basis of costs incurred to date and concludes that the variable consideration is still constrained in accordance with IFRS 15. However, on 4 December 2015, the contract is modified with the result that the fixed consideration and expected costs increase by $110,000 and $60,000 respectively. The time allowable for achieving the bonus is extended by six months with the result that Tang concludes that it is highly probable that the bonus will be achieved and that the contract still remains a single performance obligation. Tang has an accounting year end of 30 November. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above two contracts should be accounted for under IFRS 15. (In the case of (b)(i), the discussion should include the accounting treatment up to 30 November 2016 and in the case of (b)(ii), the accounting treatment up to 4 December 2015.)
Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the items above.
Professional marks will be awarded in question 4 for clarity and quality of presentation. (2 marks)
(a) Stanley Co is a frozen food processor, selling its products to wholesalers and supermarkets. From your review of the audit working papers, you have noted that the level of materiality was determined to be $1·5 million at the planning stage, and this materiality threshold has been used throughout the audit. There is no evidence on the audit file that this threshold has been reviewed during the course of the audit.
From your review of the audit planning, you know that a new packing machine with a cost of $1·6 million was acquired by Stanley Co in March 2015, and is recognised in the draft statement of financial position at a carrying amount of $1·4 million at 31 December 2015. The packing machine is located at the premises of Aberdeen Co, a distribution company which is used to pack and distribute a significant proportion of Stanley Co’s products. The machine has not been physically verified by a member of the audit team. The audit working papers conclude that ‘we have obtained the purchase invoice and order in relation to the machine, and therefore can conclude that the asset is appropriately valued and that it exists. In addition, the managing director of Aberdeen Co has confirmed in writing that the machine is located at their premises and is in working order. No further work is needed in respect of this item.’
Inventory is recognised at $2 million in the draft statement of financial position. You have reviewed the results of audit procedures performed at the inventory count, where the test counts performed by the audit team indicated that the count of some items performed by the company’s staff was not correct. The working papers state that ‘the inventory count was not well organised’ and conclude that ‘however, the discrepancies were immaterial, so no further action is required’.
The audit senior spoke to you yesterday, voicing some concerns about the performance of the audit. A summary of his comments is shown below:
‘The audit manager and audit engagement partner came to review the audit working papers on the same day towards the completion of the audit fieldwork. The audit partner asked me if there had been any issues on the sections of the audit which I had worked on, and when I said there had been no problems, he signed off the working papers after a quick look through them.
When reading the company’s board minutes, I found several references to the audit engagement partner, Joe Lantau. It appears that Joe recommended that the company use the services of his brother, Mick Lantau, for advice on business development, as Mick is a management consultant. Based on that recommendation, Mick has provided a consultancy service to Stanley Co since September 2015. I mentioned this to Joe, and he told me not to record it in the audit working papers or to discuss it with anyone.’
Required:
Comment on the quality of the audit performed discussing the quality control, ethical and other professional issues raised. (13 marks)
(b) Kowloon Co works on contracts to design and manufacture large items of medical equipment such as radiotherapy and X-ray machines. The company specialises in the design, production and installation of bespoke machines under contract with individual customers, which are usually private medical companies. The draft financial statements recognise profit before tax of $950,000 and total assets of $7·5 million.
The audit senior has left the following note for your attention:
‘One of Kowloon Co’s major customers is the Bay Medical Centre (BMC), a private hospital. In June 2015 a contract was entered into, under the terms of which Kowloon Co would design a new radiotherapy machine for BMC. The machine is based on a new innovation, and is being developed for the specific requirements of BMC. It was estimated that the design and production of the machine would take 18 months with estimated installation in December 2016. As at 31 December 2015, Kowloon Co had invested heavily in the contract, and design costs totalling $350,000 have been recognised as work in progress in the draft statement of financial position. Deferred income of $200,000 is also recognised as a current liability, representing a payment made by BMC to finance part of the design costs. No other accounting entries have been made in respect of the contract with BMC.
As part of our subsequent events review, inspection of correspondence between Kowloon Co and BMC indicates that the contract has been cancelled by BMC as it is unable to pay for its completion. It appears that BMC lost a significant amount of funding towards the end of 2015, impacting significantly on the financial position of the company. The manager responsible for the BMC contract confirms that BMC contacted him about the company’s financial difficulties in December 2015.
The matter has been discussed with Kowloon Co’s finance director, who has stated that he is satisfied with the current accounting treatment and is not proposing to make any adjustments in light of the cancellation of the contract by BMC. The finance director has also advised that the loss of BMC as a customer will not be mentioned in the company’s integrated report, as the finance director does not consider it significant enough to warrant discussion.
Kowloon Co is currently working on six contracts for customers other than BMC. Our audit evidence concludes that Kowloon Co does not face a threat to its going concern status due to the loss of BMC as a customer.’
Your review of the audit work performed on going concern supports this conclusion.
Required:
(i) Comment on the matters to be considered, and recommend the actions to be taken by the auditor; and (7 marks)
(ii) Explain the audit evidence you would expect to find in your review of the audit working papers. (5 marks)
(a) Explain FOUR factors which influence the reliability of audit evidence. (4 marks)
Andromeda Industries Co (Andromeda) develops and manufactures a wide range of fast moving consumer goods. The company’s year end is 31 December 2015 and the forecast profit before tax is $8·3 million. You are the audit manager of Neptune & Co and the year-end audit is due to commence in January. The following information has been gathered during the planning process:
Inventory count
Andromeda’s raw materials and finished goods inventory are stored in 12 warehouses across the country. Each of these warehouses is expected to contain material levels of inventory at the year end. It is expected that there will be no significant work in progress held at any of the sites. Each count will be supervised by a member of Andromeda’s internal audit department and the counts will all take place on 31 December, when all movements of goods in and out of the warehouses will cease.
Research and development
Andromeda spends over $2 million annually on developing new product lines. This year it incurred expenditure on five projects, all of which are at different stages of development. Once they meet the recognition criteria under IAS 38 Intangible Assets for development expenditure, Andromeda includes the costs incurred within intangible assets. Once production commences, the intangible assets are amortised on a straight line basis over five years.
Required:
(b) Describe audit procedures you would perform. during the audit of Andromeda Industries Co:
(i) BEFORE and DURING the inventory counts; and (8 marks)
(ii) In relation to research and development expenditure. (4 marks)
(c) During the audit, the team discovers that one of the five development projects, valued at $980,000 and included within intangible assets, does not meet the criteria for capitalisation. The finance director does not intend to change the accounting treatment adopted as she considers this an immaterial amount.
Required:
Discuss the issue and describe the impact on the audit report, if any, if the issue remains unresolved. (4 marks)
Maria:
– Is resident and domiciled in the UK.
– Is a higher rate taxpayer and will remain so in the future.
– Has already realised chargeable gains of £15,000 in the tax year 2015/16.
Shares in Granada Ltd:
– Maria subscribed for 10,000 £1 ordinary shares in Granada Ltd at par in June 2006.
– Maria is one of four equal shareholders and directors of Granada Ltd.
– Maria intends to sell either 2,700 or 3,200 shares back to the company on 31 March 2016 at their current market value of £12·80 per share.
– All of the conditions for capital treatment are satisfied, except for, potentially, the condition relating to the reduction in the level of shareholding.
Granada Ltd:
– Is a UK resident trading company which manufactures knitwear.
– Prepares accounts to 31 December each year.
– Is registered for VAT.
– Acquired the trade and assets of an unincorporated business, Starling Partners, on 1 January 2016.
Starling Partners:
– Had been trading as a partnership for many years as a wholesaler of handbags within the UK.
– Starling Partners’ main assets comprise a freehold commercial building and its ‘Starling’ brand, which were valued on acquisition by Granada Ltd at £105,000 and £40,000 respectively.
– Is registered for VAT.
– The transfer of its trade and assets to Granada Ltd qualified as a transfer of a going concern (TOGC) for VAT purposes.
– The business is forecast to make a trading loss of £130,000 in the year ended 31 December 2016.
Granada Ltd – results and proposed expansion:
– The knitwear business is expected to continue making a taxable trading profit of around £100,000 each year.
– Granada Ltd has no non-trading income but realised a chargeable gain of £10,000 on 1 March 2016.
– Granada Ltd is considering expanding the wholesale handbag trade acquired from Starling Partners into the export market from 1 January 2017.
– Granada Ltd anticipates that this expansion will result in the wholesale handbag trade returning a profit of £15,000 in the year ended 31 December 2017.
Required:
(a) (i) Explain, with the aid of calculations, why the capital treatment WILL NOT apply if Maria sells 2,700 of her shares back to Granada Ltd, but WILL apply if, alternatively, she sells back 3,200 shares. (4 marks)
(ii) Calculate Maria’s after-tax proceeds per share if she sells:
(1) 2,700 shares back to Granada Ltd; and alternatively
(2) 3,200 shares back to Granada Ltd. (4 marks)
(b) (i) Describe the corporation tax treatment of the acquisition of the ‘Starling’ brand by Granada Ltd, if no charge for amortisation was required in its statement of profit or loss. (3 marks)
(ii) Discuss how Granada Ltd could obtain relief for the trading loss expected to be incurred by the trade acquired from Starling Partners, if it does not wish to carry any of the loss back. (5 marks)
(c) Explain the value added tax (VAT) implications for Granada Ltd in respect of the acquisition of the business of Starling Partners, and the additional information needed in relation to the building to fully clarify the VAT position. (4 marks)